The Hadza people are an indigenous ethnic group in Tanzania
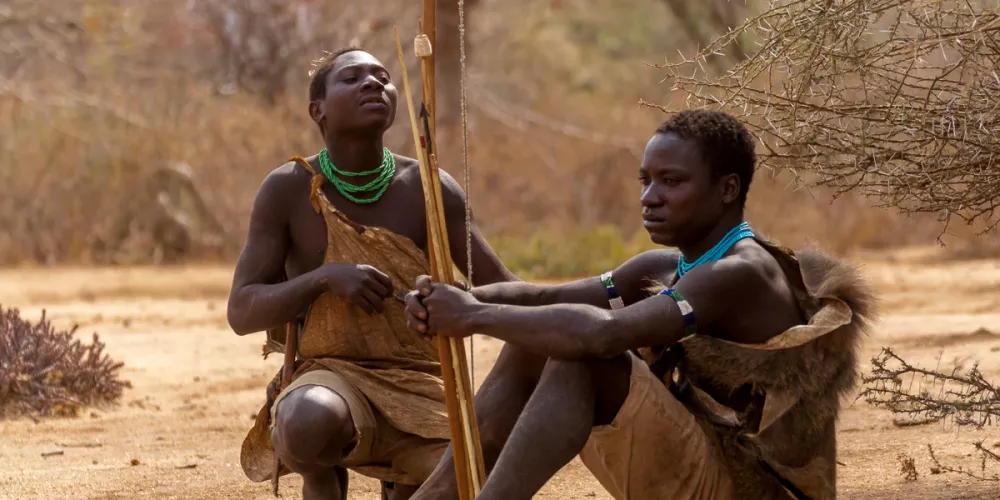
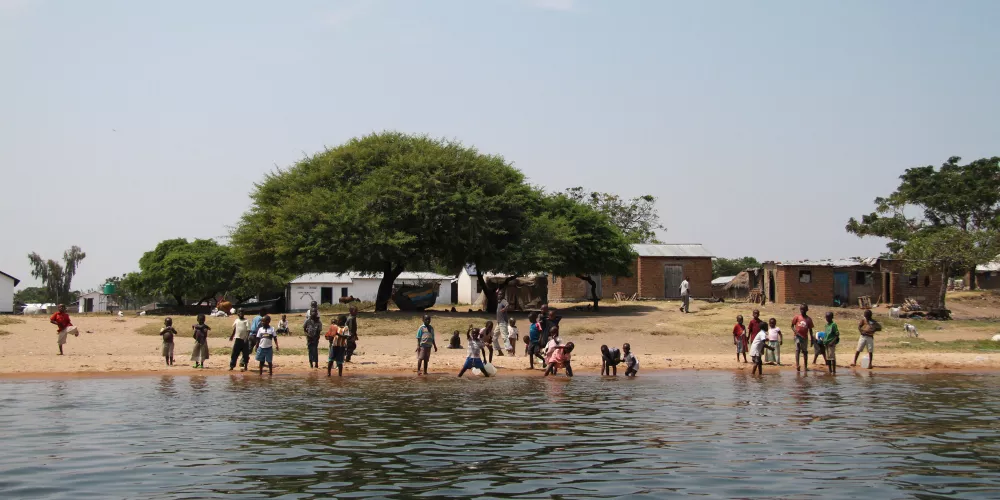
The Hadza people are an indigenous ethnic group in Tanzania, primarily residing in the Lake Eyasi region in the country's northern part. They are one of the last remaining hunter-gatherer societies in Africa. The Hadza have a unique culture and lifestyle that is closely tied to their traditional hunting and gathering practices.
Here are some key points about the Hadza people
Lifestyle: The Hadza rely on hunting game, gathering wild fruits and tubers, and collecting honey for their sustenance. Their traditional lifestyle revolves around mobility, as they move their camps frequently in search of food sources.
Language: The Hadza language, also known as Hadzane, is a click language. It is a linguistic isolate, meaning it is not known to be related to any other language.
Social Structure: Hadza society is relatively egalitarian, with no centralized political authority. They live in small bands consisting of 20 to 30 individuals, with no formal leadership or hierarchical structure. Decision-making is typically reached through consensus.
Gender Roles: Men primarily engage in hunting, using traditional methods such as bows and arrows, while women focus on gathering plant foods and taking care of children. However, both men and women participate in various tasks, and there is a degree of flexibility in gender roles.
Cultural Significance: The Hadza have a rich oral tradition, passing down their history, stories, and knowledge through storytelling and songs. They also have spiritual beliefs and engage in rituals, often centered around hunting and gathering.
Threats and Challenges: The Hadza face various challenges, including encroachment on their lands, pressure to adapt to more sedentary lifestyles, and the decline of traditional food sources due to factors like deforestation and competition with neighboring pastoralist communities.
Conservation Efforts: There have been efforts by local and international organizations to support the Hadza in preserving their culture and land rights. Some initiatives aim to promote sustainable livelihoods and ecotourism while respecting traditional practices and values.